
The Full option tells the command to perform a full format, and the -Force option specifies the override switch. If you do not know and are on Windows 10, you should use NTFS. In the command, replace DRIVE-LETTER with the correct letter reflecting the drive you want to format, and FILE-SYSTEM for FAT32, exFAT, or NTFS, depending on the file system you want to use. (Optional) Type the following command to perform a full format of the USB flash drive and press Enter: Format-Volume -DriveLetter DRIVE-LETTER -FileSystem FILE-SYSTEM -Full -Force.This example performs a quick format of the "F" drive with the NTFS file system: F ormat-Volume -DriveLetter F -FileSystem NTFS -NewFileSystemLabel workUSB. In the command, replace DRIVE-LETTER with the correct letter reflecting the drive you want to format, FILE-SYSTEM for FAT32, exFAT, or NTFS, and DRIVE-NAME with the name you want the device to appear in File Explorer. Type the following command to perform a quick format on the flash drive and press Enter: Format-Volume -DriveLetter DRIVE-LETTER -FileSystem FILE-SYSTEM -NewFileSystemLabel DRIVE-NAME.


In the "Volume label" field, confirm a drive name that will appear in File Explorer.Use the default selection in the "Allocation unit size" drop-down menu.However, if you think you might use the device on a Linux machine, "FAT32" is the best option, even though you will be limited to 4GB file sizes. Quick tip: If you plan to use the removable storage on Windows 10 as well as on macOS systems, you may want to select the "exFAT" option for compatibility.
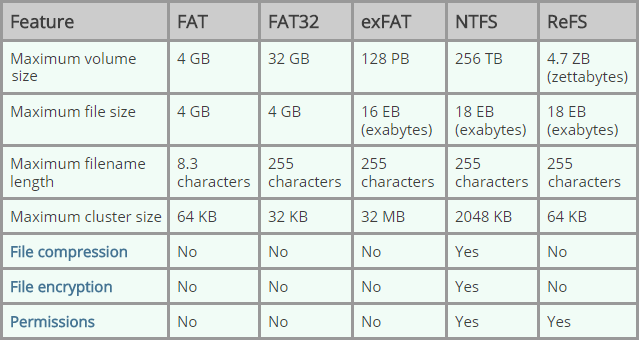
Use the "File system" drop-down menu and select the NTFS option.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
